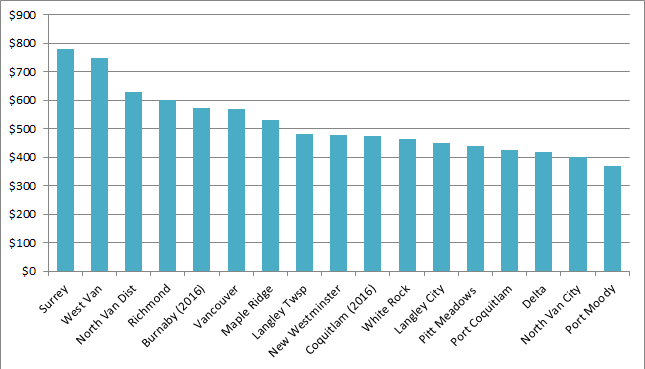
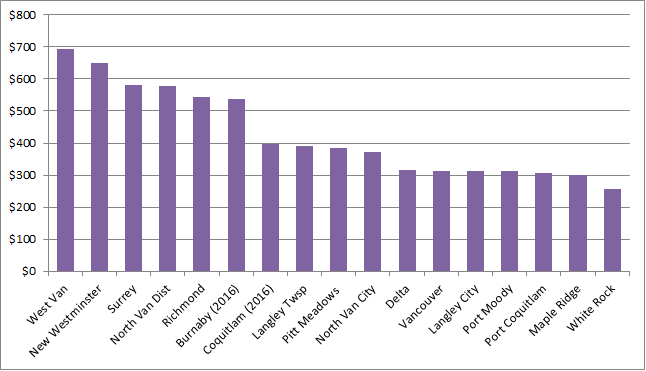
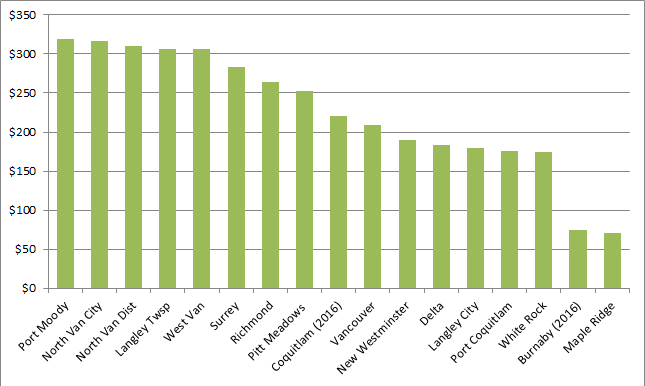
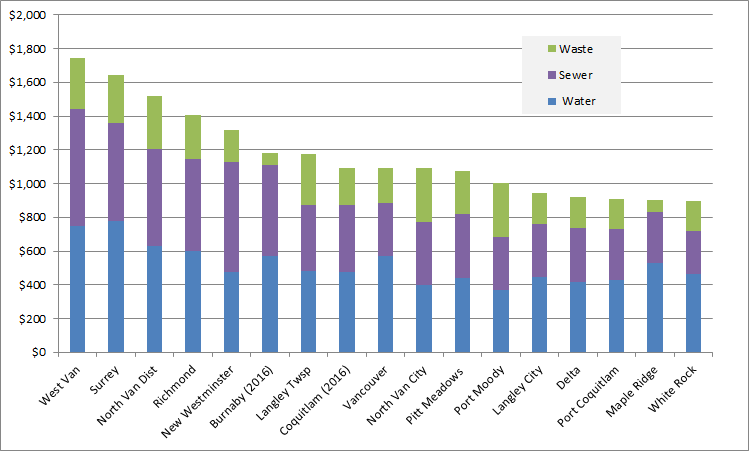
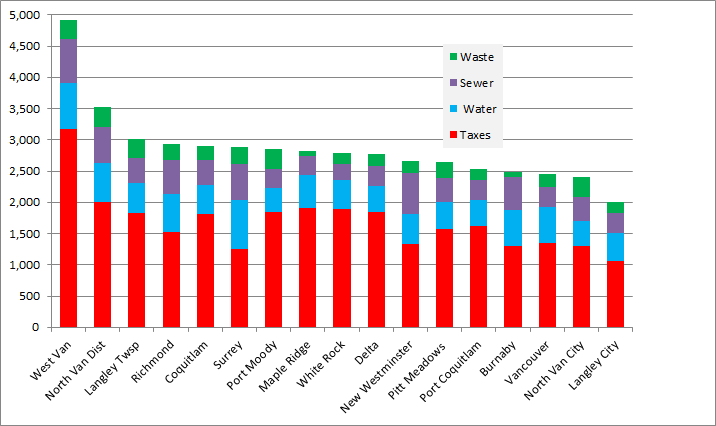
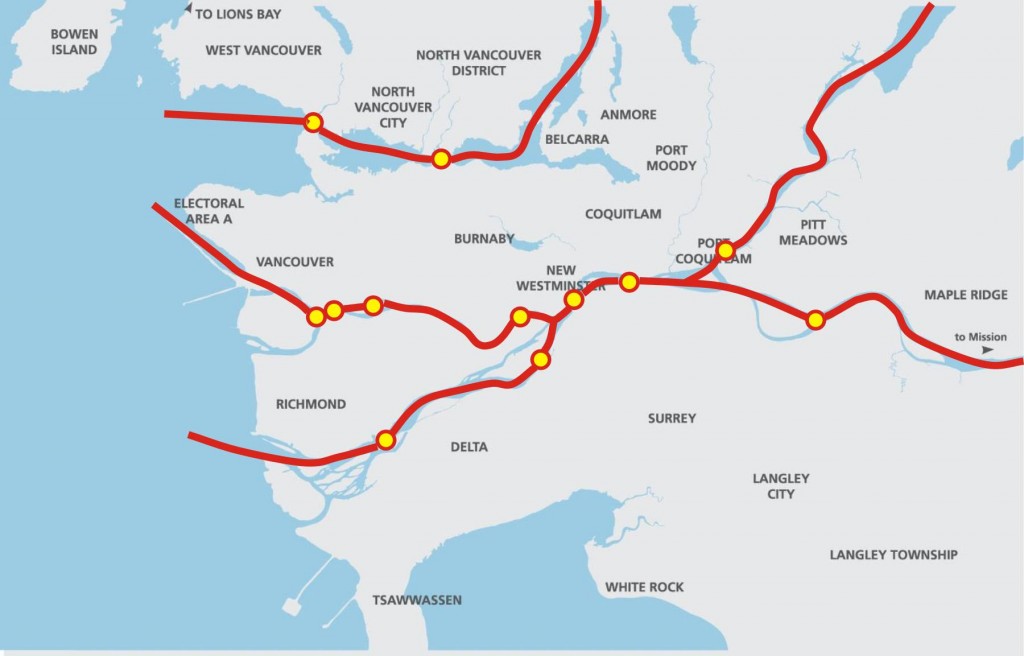
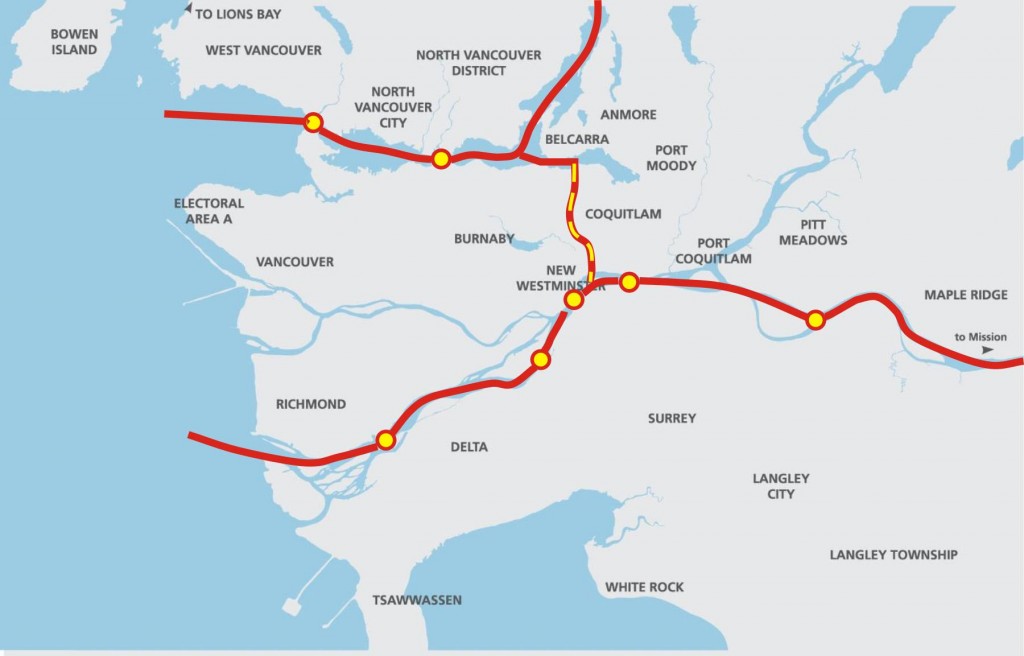
The Earth is currently warming at a rate unprecedented in recent history, almost entirely due to human activity, primarily the digging up and burning of fossil carbon and introducing CO2 to the atmosphere at a rate much faster than natural biosystems can remove it. This is not a controversial set of facts.
However, much like people who refuse to believe that natural selection shaped the evolution of life on our planet, or those that believe there could be a breeding population of large bipedal hominids lurking just out of sight in the woods of the Pacific Northwest, there are some for which this set of facts cannot fit within their political, religious, or economic ideologies. No problem, it’s a big world, reality isn’t for everyone.
Problems do arise, however, when those so separated from reality are given the power to shape public opinion and political will. I provide for your review the most recent opinion of Black Press’ go-to climate change correspondent, Tom Fletcher. I recognize the Streisand Effect of even calling attention to this bunk, but perhaps we can glean from this a teaching moment.
There is a lot in here, representative of Tom’s liberal (ahem) application of the Gish Gallop on this topic, so I will only pull out two major themes, where he brushes up against the science. I’ll touch more on the politics later.
“According to the environment ministry’s 2015 Indicators of Climate Change report, B.C.’s average temperature has increased about 1.5 degrees from 1900 to 2013, slightly more in the north and less in the south. That’s one one hundredth of a degree per year”
See how only little cherry-picked factoid stripped of context can be used to sow doubt about the seriousness of the situation? The report (which you can read here) says 1.4°C per century from 1900 to 2013 (doing the math on that strange bit of language, that means 1.6°C in the 113 years between the two dates). At the risk of pedantry, this is 40% more than one one hundredth of a degree per year – an annual change of 0.014°C.
Still, a number so small, it can’t possibly a problem, right? Except…
We can all agree the climate has changed before. During an era 10-20,000 years ago there was a dramatic climatic change that saw continental glaciation in North America come to an end. What is now British Columbia went from being about 95% covered with ice to less than 1%. No doubt this type of dramatic climate shift had devastating effects on the extant biosystems, not to mention any society that existed during that time. Some survived, others didn’t. It was monumentally disruptive.
However, that dramatic landscape-shifting shift in climate came with a 3.5°C shift in temperatures over about 8,000 years. To simplify this trend to Tom Fletcher math, that is about 4 ten-thousandths of a degree per year – an annual change of 0.0004°C. The current temperature shift is happening at more than 30 times the speed of the previous, devastating one.
Except it isn’t, because the current trend has been accelerating over those 113 years. The rate of warming now is more than twice that of the first half of the century. If one looks only at the trend from 1960 onwards (as the ubiquitous use of fossil fuels and resultant exponential increase in energy consumption has expanded from the socio-economic “First World” to the majority of the planet), the rate is not only faster, but the acceleration is accelerating.
“The B.C. report ritually attributes this to human-generated carbon dioxide, the only factor the UN climate bureaucracy recognizes. And here lies a key problem for the global warming industry.
“More than 90 per cent of the greenhouse effect in the Earth’s atmosphere is from water vapour. Antarctic ice core analysis shows that over 400,000 years, increasing carbon dioxide has lagged centuries behind temperature increase. This suggests that rising temperatures lead to increased CO2, not the other way around. (Scientific American, working hard to debunk this, found a study that shows the CO2 lag is only 200 years, rather than 800 as others calculate. Still, it can’t be causing warming.)”
A little knowledge is a dangerous thing, and the measure of Fletcher’s knowledge of this topic is most generously described as “little”. So let’s unpack that paragraph a bit and see where his failure to do his reading has failed his keenly skeptical mind.
On water vapour, Mr. Fletcher is almost right. Water vapour is indeed a strong greenhouse gas, however the behaviour or water in the atmosphere (where it enters as a vapour, exists in all three phases at a wide variety of temperatures, and exits primarily as a liquid, influencing upward and downward energy fluxes at all times) is horribly complicated. The best estimates modelling these fluxes (and I’ll refer to Kiehl and Trenberth, 1997 here) suggest water vapour represents about 60% of the total radiative forcing under clear skies, and somewhat more under cloudy skies (at any given time, the planetary cloud cover is about 62% – a pretty cool factoid to pull out at your next dinner party). There are more complications here, as we can get into debates about defining the “greenhouse effect” relative to the impact on the planet’s surface vs. that in the atmosphere, about difficulty defining latent heat fluxes from precipitation, and other details that were definitely discussed in my upper-level boundary layer climatology courses, but that was 20 (ack!) years ago, and I am not as well versed as I once might have been.
Those caveats aside, the inference by Mr. Fletcher is that water vapour is a higher percentage than CO2, and therefore CO2 doesn’t matter. Nothing could be farther than the truth.
The same estimates put CO2 forcing at around 26%, based on historic CO2 concentrations (the 1990 concentration of 353ppmv was used, although the global concentration in 2015 is at least 13% higher than this). More importantly, one needs to recognize that the two gasses exist in the atmosphere in very, very different ways.
When we emit CO2 into the atmosphere, it essentially stays there until sorbed into the ocean or is made into rock through biogenic systems – two very slow processes. Respiration by plants is, at best, a temporary storage, as the majority of CO2 that enters plants is returned to the atmosphere within a year or a decade, and almost all of the rest within a century. Stick extra CO2 in the atmosphere, it stays there for a long time.
Conversely, the concentration of H2O in the atmosphere is controlled by atmospheric pressure and temperature – because in normal atmospheric conditions H2O exists in all three phases (CO2 only exists as a gas in the atmosphere of earth- there are no conditions here where liquid or solid CO2 form naturally). Stick more H2O in the atmosphere, and it exits again almost immediately as rain or snow when the saturation level of the air at that temperature and pressure is met. If we double or treble human inputs of H2O into the atmosphere without changing atmospheric temperature, the net concentration of H2O in the atmosphere a decade later will be unchanged (notwithstanding the sheer enormity of the natural H2O cycle of evaporation and precipitation, where the most generous estimates of human inputs account for something like 0.005%).
So the only thing we can do to influence that 60% of forcing is to increase the temperature of the atmosphere (as meaningfully changing the pressure of the atmosphere, globally, is beyond our current terraforming technology). In contrast, by effectively doubling the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere, we are wreaking havoc with that 26% of forcing – it is going up. And that’s the part we are talking about.
Now, onto ice those pesky ice cores. Those pre-industrial atmospheric CO2 changes over the last 400,000 years did lag behind temperature increases (by how much is a debated point, see Caillon et al, 2003). That should actually frighten us, not make us confident. It also in no way refutes the observation that anthropogenic combustion of fossil carbon is the primary driving force for the current temperature increases.
When the ice in those cores was being deposited (and ice cores are not the only temperature/CO2 proxies we have, but let’s keep this simple) it was recording long-scale shifts in global climate caused by Milankovitch cycles. Short version: cyclic wobbles in the axis of the earth’s rotation relative to the sun along with changes in the shape of our orbit give rise to 100,000-year long cycles of increased and reduced solar input. These shifts continue today, indeed we are just past a “peak” that occurred ~10,000 years ago, and are in the downward part of the cycle with solar input slowly decreasing right now. Global CO2 levels also shift in lockstep (or slightly after) these cycles, from 180ppm to 290ppm.
I cannot emphasize this enough – the historic climate effects of Milankovitch cycles occur at a rate orders of magnitude slower than what we are currently observing: Heating at a scale of 0.0005°C per year, cooling at a rate of 0.0001°C per year.
These historic shifts in temperature were not caused by changes in greenhouse gasses, and no-one has suggested they are. They are caused by shifts in the solar energy hitting the earth. So the cause of the much slower heating and cooling cycles recorded in the ice cores is not, in any practical way, related to the cause of the much faster heating today. They are two separate phenomena, operating in different ways, at different scales. To compare them is like comparing the tide coming in to a tsunami – both cause the sea to rise, but in different ways, through different processes with, different effects.
So Fletcher is right- the initial cause of warming 25,000 years ago, 130,000 years ago, 250,000 years ago, was not CO2, but that does not mean the cause of the present warming isn’t CO2. In fact, we know it is.
More problematically, the ice cores demonstrate that increases in temperature related to outside causes can (and do) result in increased atmospheric CO2, for a bunch of reasons relating to carbon storage in soils and the sea. This, in turn, creates a positive feedback loop. As the earth gets warmer, more greenhouse gasses (GHG) are released, and that increased GHG concentration warms the earth further. This is the primary reason why the cooling phase related to Milankovitch cycles operates at a quarter of the speed of the heating phase – once that GHG blanket is thrown over the warm earth, it takes much longer to cool off.
That should scare us, as should the other data from the ice cores. Even at the “peak” of the previous cycles observed in the ice cores, planetary CO2 was only 290ppm. We are now over 400ppm, and the trend is continuing up. It also means that once those GHG hit the atmosphere, their effects are long-lasting, and getting back to start gets much harder the further we move away from what I can only loosely call a “baseline”.
In the end, the reality of this information doesn’t matter. No amount of science-based explanation is going to change Mr. Fletcher’s mind about this topic. He will continue to believe that the hundreds of thousands of scientists at NASA, NOAA, the American Geophysical Union, the American Meteorological Society, the Royal Society, the U.S. National Academy of Science, (and every other national academy of science on earth, from Bolivia to Zimbabwe), are either pulling a monumentally complicated con only he and a few of his buddies can see through, or are fools lacking his brilliant insight into global climate systems.
His views are so separated from reality that he may as well be casting Bigfoot footprints, and should be treated as a crackpot. Instead, he is paid for his misinformed opinion, which is subsequently circulated widely throughout BC, as the lead columnist for the only newspaper that much of BC ever sees: their local Black Press iteration resulting from our era of old media consolidation.
Although the facts of anthropogenic global warming are strictly scientific, discussing these facts is unfortunately political, because the implications and any solutions to address them will require political will. By using his bully pulpit as one of the most widely-distributed columnists in the province and President of the Legislature Press Gallery to spread misinformed crackpottery about this topic, he deliberately undermines the political will required to take action. He helps relieve our leaders of the responsibility to lead. His ongoing efforts towards agnotology are a real disservice to his industry, and the public he claims to inform.



 There is no doubt the Ministry has talked to many people, but to say they have “consulted” is quite the stretch. The City where the majority of the project has taken place
There is no doubt the Ministry has talked to many people, but to say they have “consulted” is quite the stretch. The City where the majority of the project has taken place 

 This may very well be true. But you know what is cheaper than building a new tunnel and cheaper than a new bridge? Making the infrastructure you already have work better. One of the more galling parts of this entire project is that no-one seems to be looking at the opportunity cost of a $3.5Billion infrastructure investment – what real improvements could we build to the regional transportation system with that kind of money.
This may very well be true. But you know what is cheaper than building a new tunnel and cheaper than a new bridge? Making the infrastructure you already have work better. One of the more galling parts of this entire project is that no-one seems to be looking at the opportunity cost of a $3.5Billion infrastructure investment – what real improvements could we build to the regional transportation system with that kind of money. 


 Did you know that Highways are allowed in the ALR? Much of the South Fraser Perimeter Road is actually in the ALR, no exclusion necessary, just compensation paid to the property owner who has his acreage bisected or cut off. So the Ministry can put the entirety of this project on ALR land and claim “no net loss” of ALR land- although admittedly it is hard to farm asphalt.
Did you know that Highways are allowed in the ALR? Much of the South Fraser Perimeter Road is actually in the ALR, no exclusion necessary, just compensation paid to the property owner who has his acreage bisected or cut off. So the Ministry can put the entirety of this project on ALR land and claim “no net loss” of ALR land- although admittedly it is hard to farm asphalt.