Last Monday, our Council meeting included giving three readings to a Bylaw that changed the zoning of 422 Sixth Street. The boring, technical part is that the change involved taking what was permitted on the site (Commercial Zone C3-A, high-rise commercial and mixed use commercial and multifamily residential) and add to this “supportive housing” among the long list of permitted uses. But when it comes to providing dignified housing for people in need, nothing is ever boring. As this is emblematic of the entire regional housing crisis, and as Council spent several hours over several meetings putting up and taking down red tape around this simple land use change, I am going to spend some time unpacking this project timeline and Council’s decision making.
As this project is a bit of a hot button, I am going to once again remind folks this is a blog, not official City communications. Though I try my best to stick to the facts, everything here is my opinion and filtered through my memory and notes, and not written by or edited by anyone at the City, or anyone else for that matter.
The proposal that came before Council from the owner of the building at first seemed like a simple one. They have a four-story building where they operate offices on the bottom two floors. The two upper floors are underutilized and the current zoning allowed housing in those upper two floors. The owner has provided a variety of services around the region for more than 40 years (Childcare, food hamper programs, youth services, health and education programs, and housing). There is a desperate need for transitional/supportive housing in New West (according to our updated housing needs assessment, 358 units are needed by 2031, 35 a year), this operator had space, so they applied to senior government for funding to fulfill this need. They were awarded provisional funding by CMHC and BC Housing on the strength of their proposal, but needed zoning approvals by July first to add “supportive” to the already-allowable “housing”. And here we are.
Back in 2021, City Council brought forward OCP and Zoning Bylaw changes under the title “City-Wide Crisis Response” that were meant to make it easier for the City to respond with land use changes that are in support of addressing a Public Health Emergency or recognized Regional Crisis. Around the same time, the Province changed the rules to no longer require Public Hearings for zoning changes that are consistent with the OCP. When people talk about “streamlining” and “cutting Red Tape” to speed up approvals of affordable and supportive housing, this is what it looks like when the rubber hits the road.
The net effect of the changes above is that “No Public Hearing” is the presumptive default for OCP-compliant projects, though Council could move to have one if they deem it in the public interest. As a practice, New West is not having them for projects that are directly addressing stated Council priority (like addressing crisis-level need) and are compliant with the City’s Official Community Plan. This is an important step because it removes some of the uncertainty of the process at the very last stage of approvals. This does not, however, mean we are taking the public out of the process completely, but instead we will rely on earlier consultations that engage public concerns at an earlier stage in planning where issues can be meaningfully addressed. This is not without challenges (e.g. how early? A project needs to be developed far enough that there is something useful to engage the community on before we engage them; timing for senior government funding is often very, very tight, meaning consultation must occur faster than ideal), but ultimately it is a more meaningful engagement, and creates more certainty for the developer and the community.
The proposal for 422 Sixth Street first came to Council on May 8, and indeed had a tight timeline to approval, as the major senior government funding source required that zoning be put in place by the end of June. This was a fast timeline, but considered viable because the rezoning request was relatively small from a land use standpoint (again, the proposed use is aligned with the OCP and housing was already a permitted use above grade, just not “supportive” housing). After all, zoning is about land use.
At the May 8 meeting, there were a few minor questions raised regarding loss of office space, windows, and property tax implications, but no changes to the project or additional conditions were applied at the time, and Council unanimously agreed to move the project forward notionally and without a Public Hearing.
Staff then went ahead and launched a Be Heard New West page to elicit feedback on the project, put out social media calls for comment, placed an ad in the May 11 Record (where this topic was also the front page story), and sent a mailer to every household and business within 100m. All were asking for feedback by May 25 (two weeks) so the follow-up report could be prepared for the May 29th meeting, but also let folks know they could email or call or drop by City Hall for more info after this date.
Unfortunately, this is when a pamphlet prepared and distributed by an anonymous member of the community was circulated that provided misinformation about the project, raising concern for some residents or local businesses. The pamphlet curiously asked people to send feedback to me and to Councillor Henderson(?). This prompted a second City mailing to local houses and businesses correcting the record on some of the misinformation in that leaflet, and reminding people about where they could get their questions answered or provide feedback to Staff, Mayor and all of Council.
The project came back to Council on May 29th. This time I was clear with Council that this was the best opportunity to make changes that informed the Bylaws, if changes were requested. There was a staff report, we had some public delegations both in favour and opposed to the project, and a lengthy discussion at Council. Unfortunately, much of the misinformation in the pamphlet was also present during this meeting, as discussion included calling into question the capability of the operator (who has been operating in the City for 40 years), and vague inquiries about how undefined “problems” with the operator or residents would be addressed if they arise.
In the subsequent deliberation, there was a motion to add back in the requirement for a Public Hearing, which was not supported by the majority of Council. However, in light of the pamphleting, there was a request by Council to instead have genuine engagement and a dialogue with the community about the project. This included consideration of the introduction of a Community Advisory Committee and Good Neighbour Agreement on the model for the Mazarine Lodge. This latter motion for further public dialogue was supported by a majority of Council, but notably not by the members of Council who were asking for a Public Hearing. There was then a motion to move this project forward and bring Bylaws for Council deliberation after that public dialogue occurs. This motion passed (otherwise, the project dies here) but was also opposed by the two members of Council who supported a Public Hearing.
City staff put together two dialogue sessions, one in person and one online. I, along with several members of Council, attended both. I was also happy to see that many of the people who attended the council meeting on May 29th to oppose the project attended that session, and were able to engage in dialogue about their concerns. There were some excellent questions asked, and some challenges highlighted. The folks I shared a table with were happy to hear the details, and to hear that some of their concerns were unfounded based on the actual model of the project. I’m not going to say they all left in support of the project, I know some did not. But I did hear from several that the opportunity for a Community Advisory Committee was something they supported. Others I know went from totally opposed to still skeptical but willing to hear us out. I walked away feeling that we had the kind of two-way dialogue that would never have occurred at a Public Hearing, and that suggestions brought forward would result in a stronger Good Neighbour Agreement, and subsequently, a stronger project.
At the June 26 meeting of Council, staff reported back on those dialogues, and also brought Bylaws for Third Readings. This resulted in a two hour deliberation, and it got procedurally complicated. I’ll try to unpack as best I can.
As part of Council’s earlier direction, a preliminary Good Neighbour Agreement was taken to the public engagement, and drafted in collaboration with the service provider. At the June 26 meeting, two members of Council put forward amendments to the GNA, which was potentially problematic at this stage in the discussion, as the GNA was something developed collaboratively and with community buy-in. Making additions now around the details of staffing or how (if it was the desire of Council) to make the GNA binding as opposed to a voluntary agreement violated the spirit of those collaborative discussions. Worse, these amendments were being offered at a time that left no time to engage again with the Provider or funding governments about the impact of operational changes on the viability of the project, while timing on making them binding is especially problematic at this stage. This led staff to consult in camera and recommend to Council that tying the GNA to the Business License would be the most likely process to make it binding from a City functioning point of view.
On balance, Council did not support the majority of the proposed amendments, for a variety of reasons. I personally opposed these motions on their face (they mostly, in my opinion, frame people needing housing as people who need to be policed as opposed to people who need to be supported, which I find abhorrent), but also because this process was a violation of the mutual respect and collaboration that allows non-profit transitional housing providers to operate in the City. They are not an enemy to be contained, they are a provider of life-saving supports to be worked with. As such, it is a violation of the very Good Neighbour Agreement model that was being proposed here, which was already a demonstrable success in our community.
Council instead moved to support the implementation of the GNA and the Community Advisory Committee as voluntary collaboration tools that were developed through the community consultation process, as opposed to regulatory tools tied to the business license. The members of Council who proffered a number of amendments to the GNA voted in opposition to this.
Finally, the Bylaws were brought to Council at the end of the meeting for Three Readings, and Council unanimously supported the approval of the three readings. In a subsequent meeting on June 30th, the members of Council who were present (one had an excused absence for a family situation, two simply failed to show) unanimously voted for Adoption of the Bylaws, meaning the rezoning is approved.
In the end, the goal here is to provide housing that is needed in the community. This project is only 30 units, small in comparison to the need demonstrated in our Housing Needs Report, but it is also a vital piece in the housing puzzle – transitional units that help people move from shelter to more permanent affordable housing, or keep people from ever entering the shelter model. The model was not perfect, but it was approved by BC Housing for operational funding and by the Federal Government for capital funding, so it is a model the two levels of government are willing to support, and is vastly superior to having 30 fewer transitional housing units in the City. The tight timelines are (alas) a necessary result of our need to work within the Province of BC and Government of Canada funding models. This is what it looks like to work with those senior governments.
The rezoning here is specifically related to this being “supportive housing”, meaning the residents will be assured of having supports or wrap-around care if they need it, something they would not get from a private hotel SRO model, and cannot be provided consistently though the shelter model. This, along with fast-tracking and reduction in red tape for the development of non-profit housing that fully conforms with our OCP, are actions that were supported in the platforms of every single person who was elected to New Westminster Council. It was disappointing to see so many last-minute hurdles and Red Tape put in the pathway to approval of this project.
That said, I am really proud of the work Staff did to quickly pivot to a more collaborative and respectful community dialogue about the project when faced by a disinformation campaign in the community. It is this kind of dialogue that builds trust in the community that will make approval of future projects easier. It demonstrated the difference between a (by design) confrontational Public Hearing and a (well designed) dialogue with the community.
I especially appreciated a delegate coming to Council on June 26th to speak about their experience as a young parent in Queensborough through the approval, opening and operation of the Mazarine Lodge. They spoke of the fears that were spread in the community during that approval process, how they were addressed by the provider, residents, and community meeting together and having a process for dialogue, and how their entire community has benefitted. This is a model that works, and breaks down the stigma related to people who, after all, just need a home.
Good work, New West.
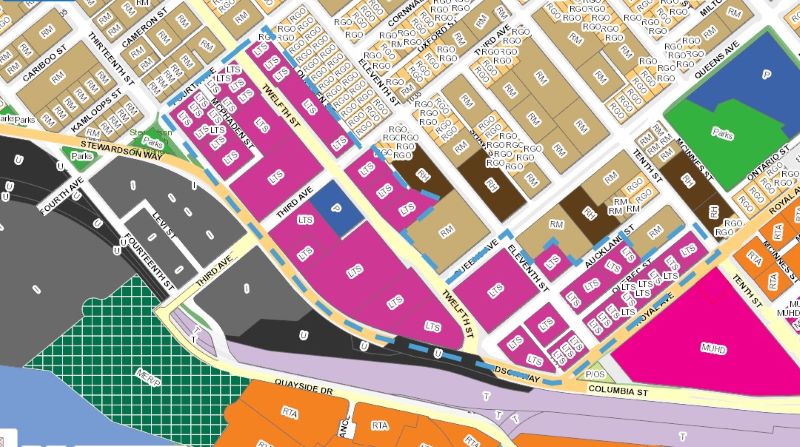
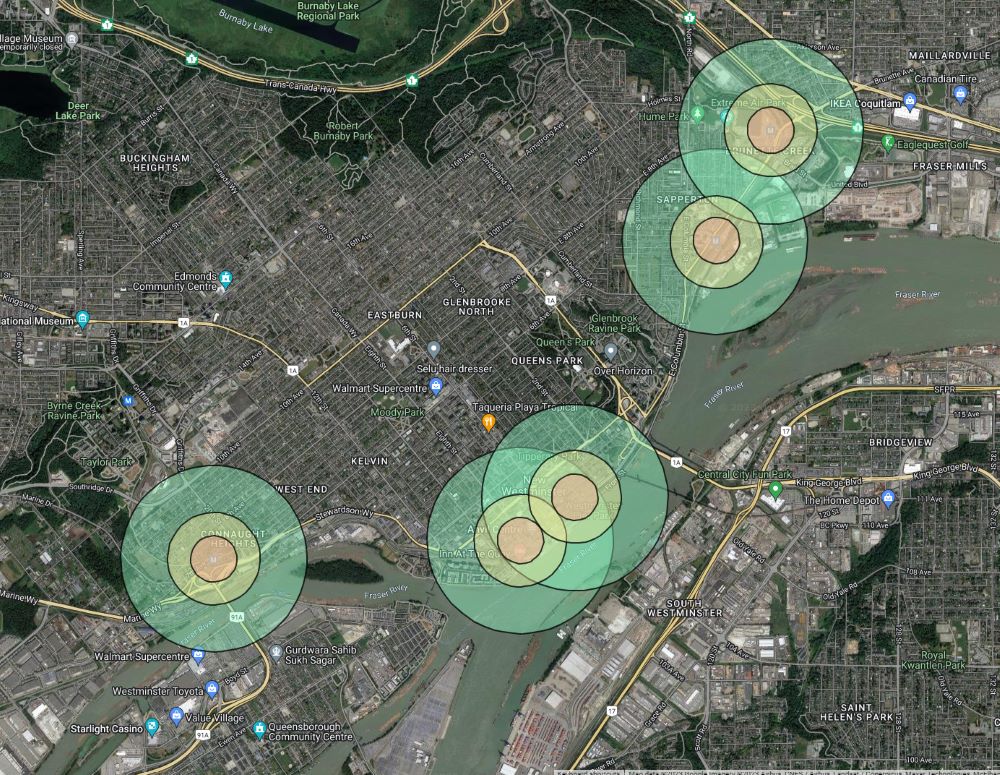
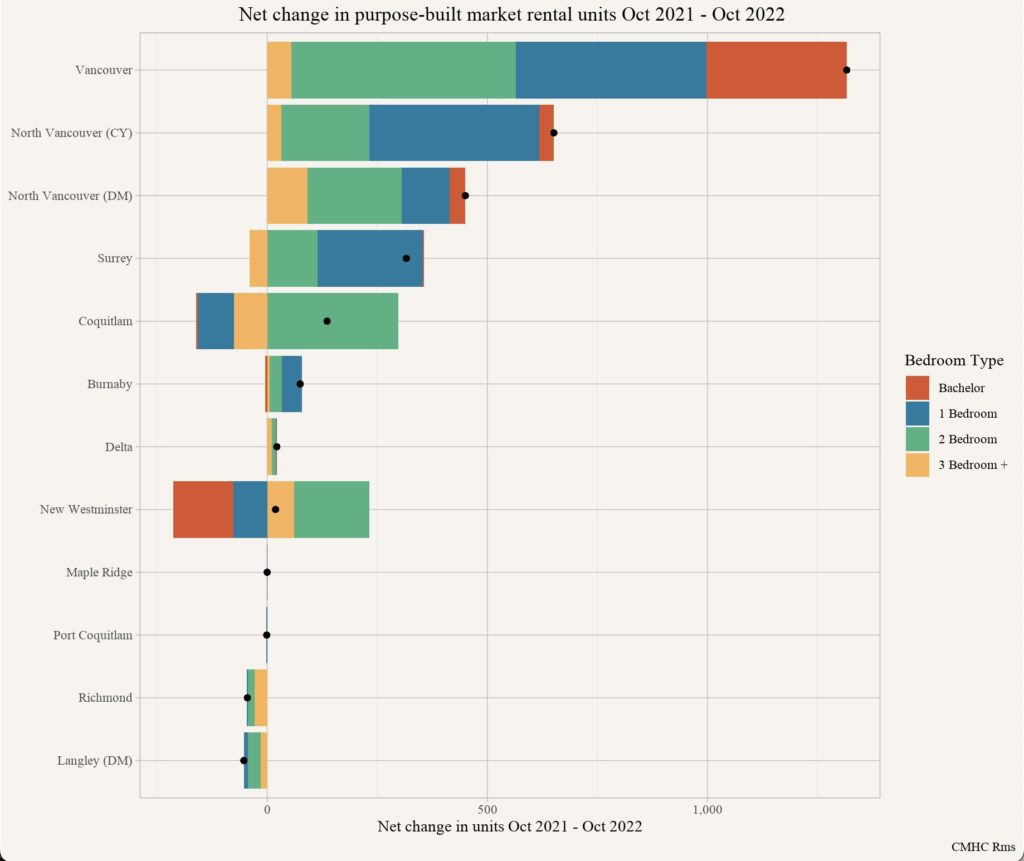
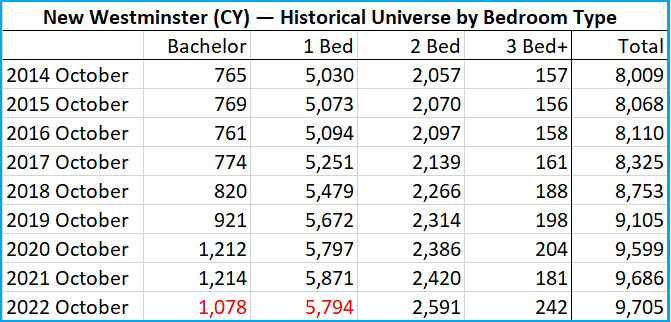
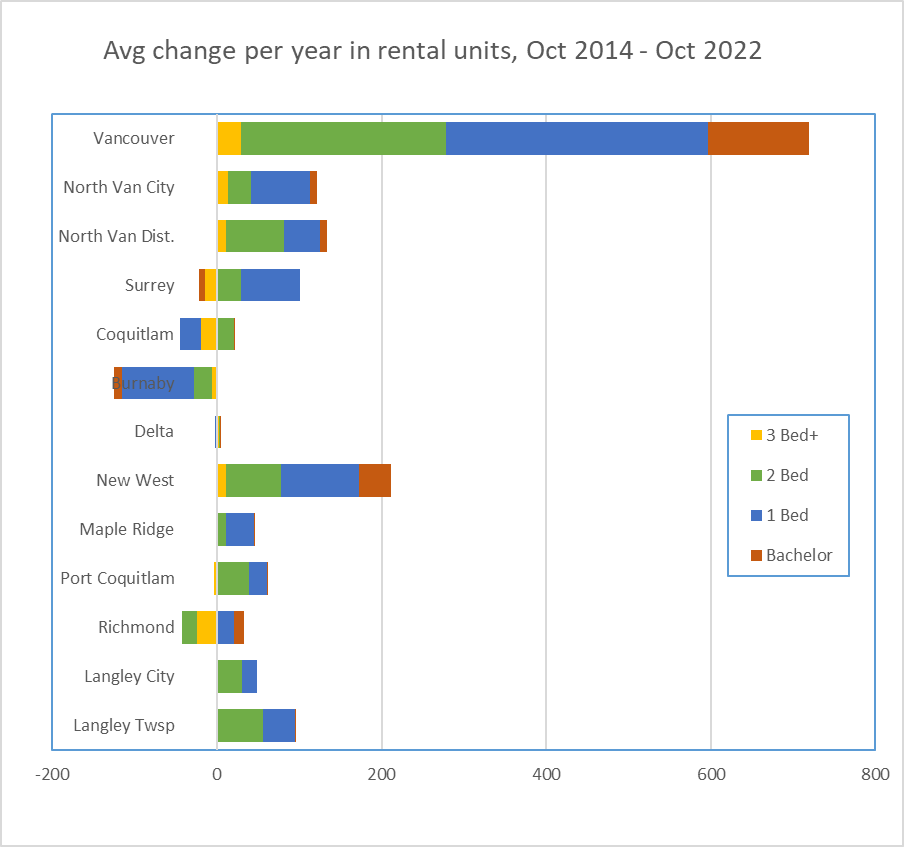
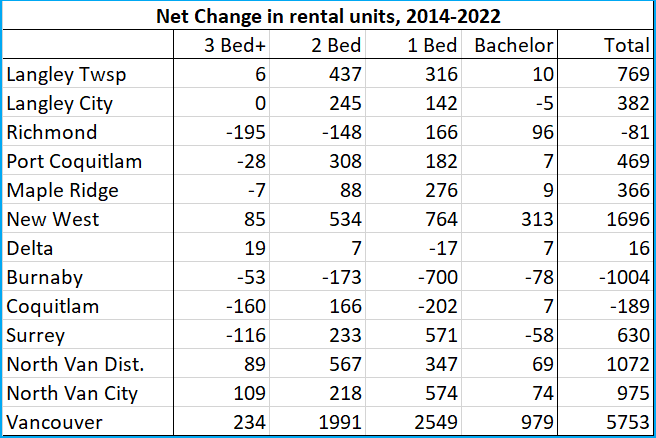
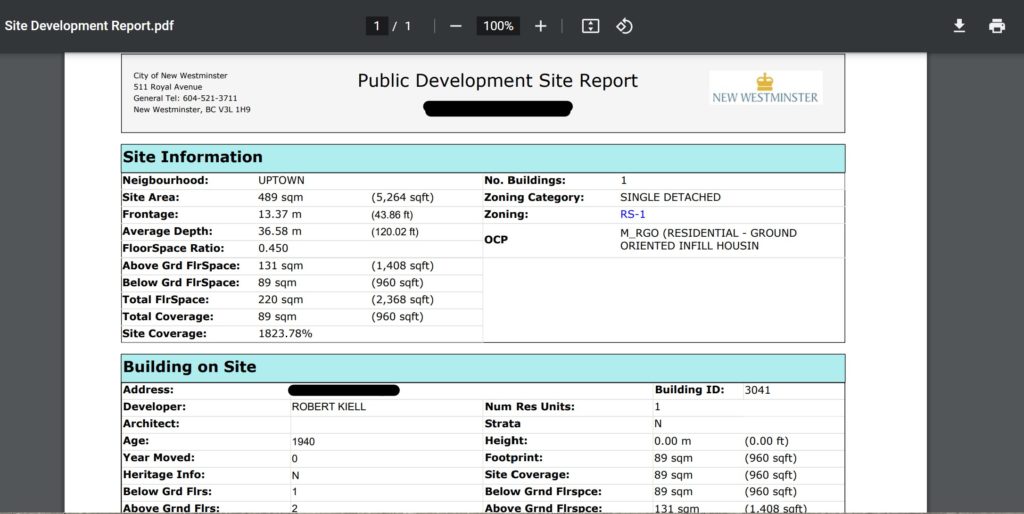
 …enter your address and get a quick report on your house. It looks a little like this (note some redacted stuff because for some reason, it is de rigueur for folks to redact publicly available information like this to make it look like we are protecting our privacy):
…enter your address and get a quick report on your house. It looks a little like this (note some redacted stuff because for some reason, it is de rigueur for folks to redact publicly available information like this to make it look like we are protecting our privacy):