I’ve been thinking about the Agricultural Land Reserve (ALR) and the Agricultural Land Commission (ALC) a lot recently. For several reasons.
Caveat: Although dealing with ALR issues is a (very small) part of my job, nothing I write here is related to actual experiences on the job, nor do I does it relate whatsoever to the opinions of my employers.
We were out on our regular every-Sunday-morning-in-a-month-without-an-“r” Fraser River Fuggitivi ride to Steveston, and a friend starting asking me about farms in Richmond. Among the topics: “wow, farmers must be rich, these huge houses!” and (in response to some signs on a farm) “is illegal dumping a really an issue?”
A second reason it has been on my mind was my recent short tour of Urban Digs Farm in Burnaby. We were there to buy some locally-grown and humanely raised pork, but got an impromptu tour and learned a lot about the realities of small farming in the Urban ALR.
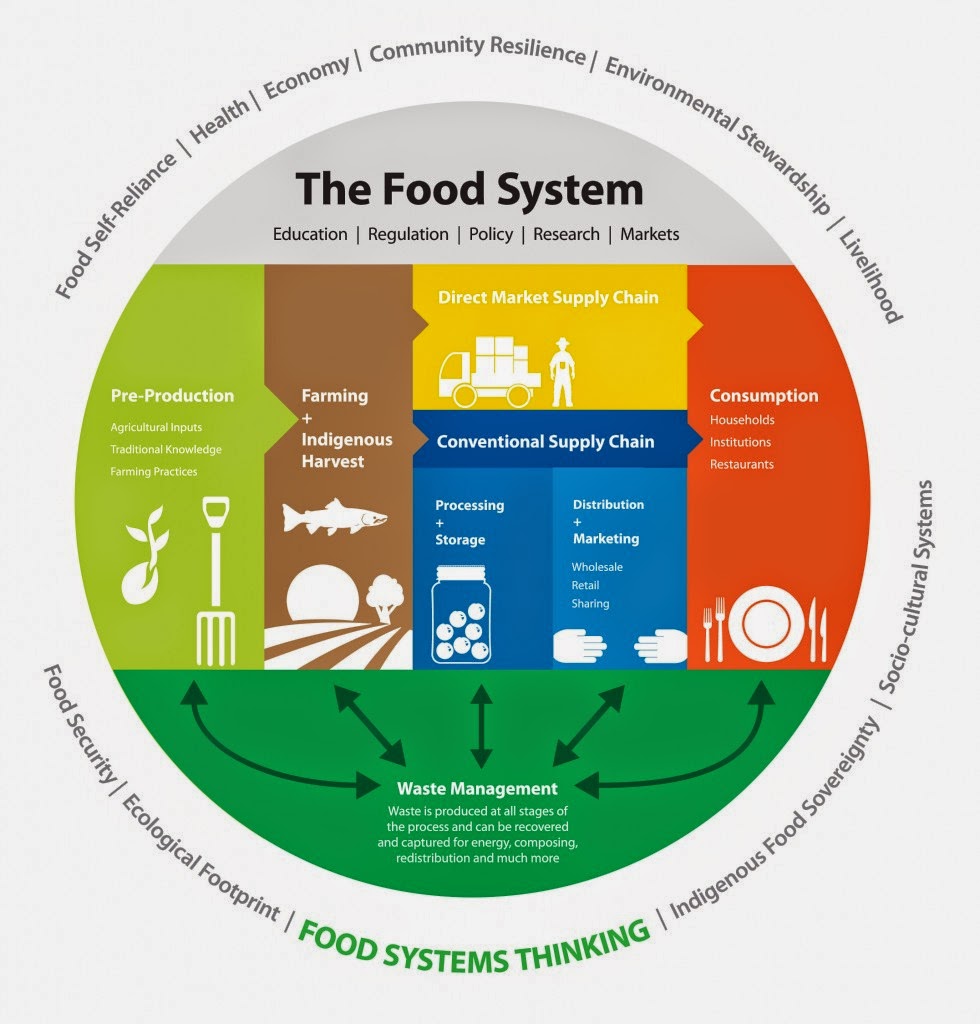
Thirdly, I recently saw a presentation by Kent Mullinix about the Southwest BC Bio-Regional Food System Design Project. This is a science-based collaborative investigation of the BC food system, with an emphasis on the sustainability of the inputs (soil, water, nutrients) and outputs (waste) of our local food supply.
All of these ideas were entering my already-addled head, because they entered in the context of the current discussion happening in Victoria about changes to the Agricultural Land Commission. The more I learn about this topic, the more concerned I am about the erosion of our ability, as a society, to feed ourselves, and the ripple effects that will have in our local and regional economy.
So let’s go back up to topic #1: The economics of farming in parts of the Lower Mainland. The reality is that some people are making money farming in the Lower Mainland, but they aren’t building mansions. Well, a few are building mansions because they are the very few large landowners and leaseholders growing cranberries or blueberries at a scale and scope that they can tie into the globalized agri-business model. Most of the mansions you see on agricultural land are not owned by the farmers of the land, but people who want to build a 20,000-sqft house, and a 10-acre piece of farmland is the most affordable way to do it. The farming that occurs on that land is not by them, but by someone else (usually the agri-business conglomerates) that lease the land, allowing the person who can afford the 20,000-sqft mansion to avoid paying too much tax.
There is also a fair amount of good farmland in the Lower Mainland that is sitting idle – not being farmed because it is owned as a long-term investment. Occasionally, someone decides the land has to be raised to grow crops (often, a dubious argument) and gets approval to bring fill onto the land from the ALC. That can be very lucrative, as it is surprisingly difficult to find somewhere to put all of the dirt you dig out of the ground when you build a high-rise tower in Burnaby or Surrey or New Westminster. Occasionally, this fill is contaminated or contains construction trash or debris. Since the ALC currently does not have an Enforcement Officer in the Lower Mainland, the chances of anyone getting in trouble for dumping this non-farm-use soil on ALR land are pretty slim. Very occasionally, unknown people dump large quantities of fill of unknown quality or origin on unoccupied farmland. See the part above about “Enforcement Officer”.
The third category of farmland use in the Lower Mainland is the small farmer trying to grow crops for local markets and maybe trying to latch onto the side of the global agri-business train. For them, the work is hard, and the economics dire.
Part one of the sketchy economics are land prices. Large tracts of ALR land in the Lower Mainland can be had for $100,000 acre, if you are buying a very large piece out in the far reaches of Langley or an unimproved piece of South Surrey. If you want to buy a smaller 5- or 10-acre ALR lot closer to urban areas, your land price can get up to $1,000,000 per acre. When the vast majority of BC Farms make less than $100,000 in annual revenue, there is simply no opportunity to support that land value.
So why is the land so valuable if it doesn’t deliver revenue? See the two examples of ALR land use above. If you want 40 acres upon which to build a 20,000-sqft mansion, $6 Million seems like a bargain, especially as you can lease 75% of the land to an agri-business and save on your taxes. Add to this the speculation that all ALR (especially the stuff near urban development) has the potential to turn into extremely valuable commercial or industrial land, if you can only convince the ALC to let it out of the ALR. The speculative value of the land is so much higher than its monetary value as farmland.
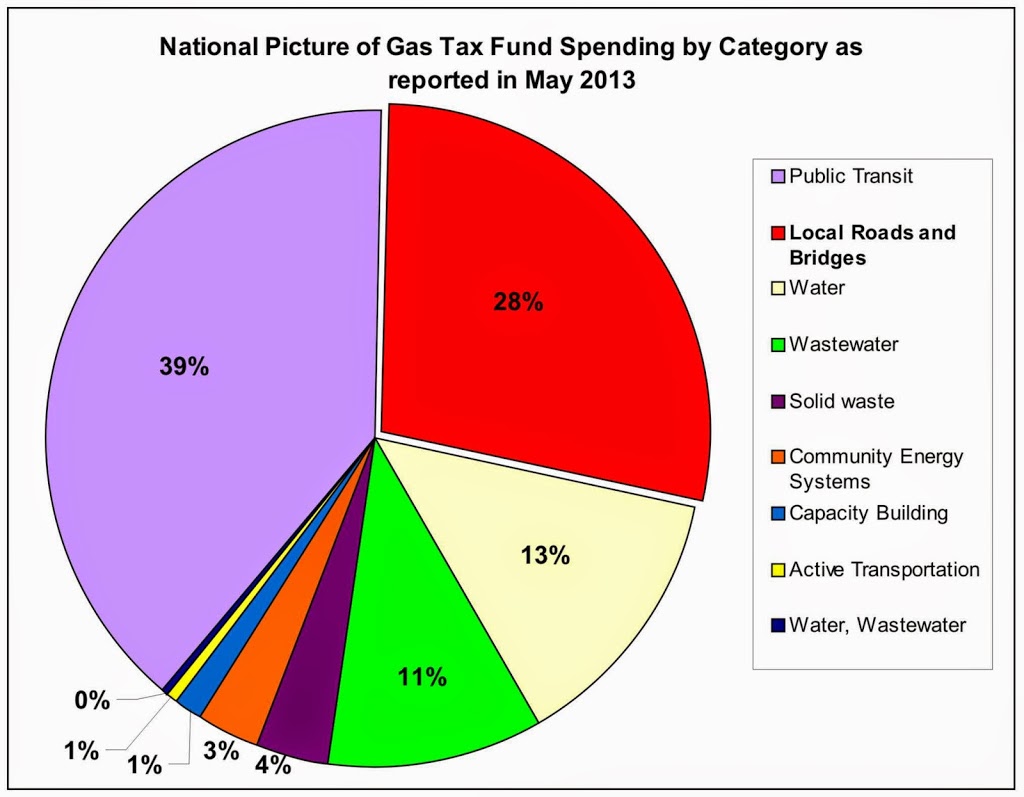
The second half of this sketchy economics discussion is the globalized agri-business industry in BC as a whole. According to Kent Mullinix, Food agriculture on BC made about $2.5 Billion in revenue last year, but the industry as a whole lost $87 Million. That is only a 3% loss on revenue – an industry can rebound from this type of temporary setback – except it is not temporary, it is systemic. The trend is downward, with no plan to recover.
The trend is going that way because the North American agriculture system is becoming less sustainable. It relies on uncertain hydrocarbon markets to fuel it, it is overtaxing the soil, in some places depleting the ground and surface water that sustains it, in other areas polluting the water running off from it. It is becoming more reliant on a few large Corporations that own all of the seeds and the pesticides that the seeds have been genetically modified to tolerate. The meat is overloaded with antibiotics that are creating a resistance problem, and grown in such concentrated conditions that the entire Fraser Valley has a “nutrient glut” – they can’t find anywhere to put all the shit they are generating. If, god forbid, there is a bumper crop, the Global Market, in all its invisible-hand wisdom, causes prices to dive and the farmer still struggles to break even. Margins are so tight that an entire industry of indentured servants temporary foreign workers had to be developed to allow the money-losing crops to get to export.
This contrasts completely with the approach the good people at Urban Digs are taking. They have leased a few acres of land in the last remnants of farm land in Burnaby, and use it to grow higher-value vegetable crops, organic free-run chickens (for eggs), ducks (for meat), and pigs. They may grow other things, but those what was on site when I visited.
I first met Julia from Urban Digs when we both presented at the same PechaKucha event at the River Market. I babbled on about rocks, but she gave a compelling talk about the farm that struck a nerve when she discussed the ethics of meat eating. She spoke of raising, nurturing, and caring for animals before you slaughter them for meat. Short of becoming an ethical vegan, this seems the least cruel way to manage our meat supply. Also, because they are not stressed, are free to roam, and have healthy balanced diets, the meat simply tastes better. Yes, this meat is a little more expensive than the foam-platter plastic-wrapped slab of flesh at Safeway… but I’ll address that issue later.
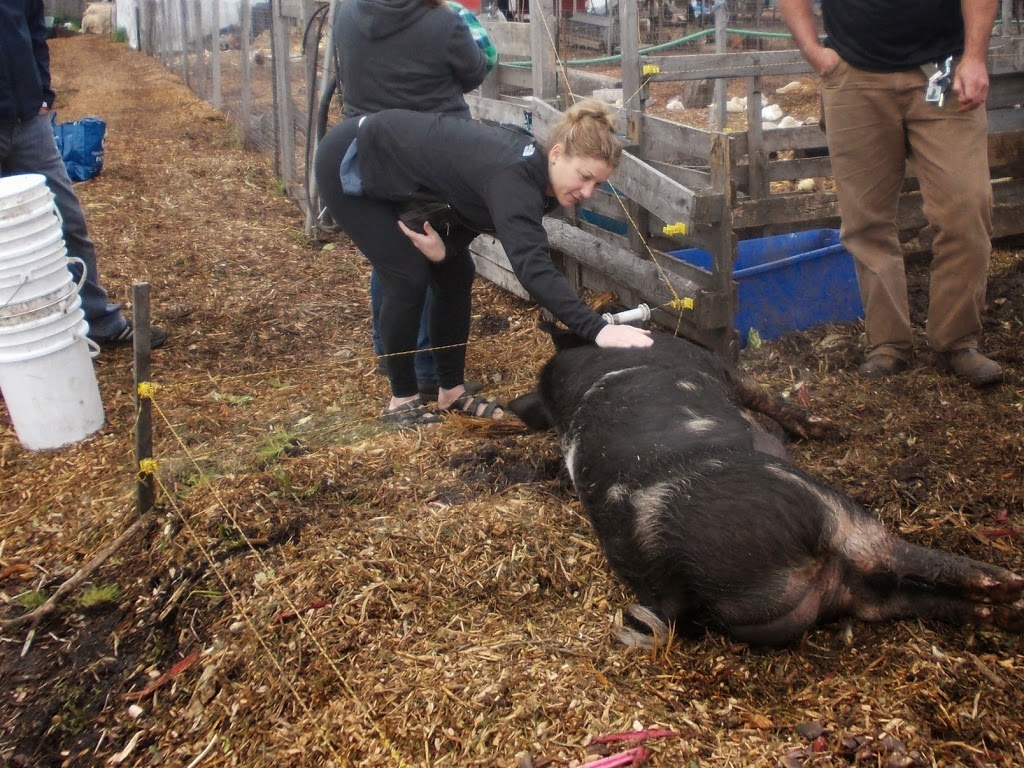 |
| That’s MsNWimby meeting her meat at Urban Digs. |
Urban Digs are like pretty much every successful small-business owner I have met: They bust their ass every day to keep things running; They hire a local assistant when they can afford it and need arises to share in the hard work and they pay them for it; They rely on an integrated network of local supports for the bulk of their supplies; They are constantly reaching out to expand their local customer base and innovating to find new ways to serve their market. They contribute to their community, and every dollar they make is returned to the local economy. They are not getting rich, aren’t building a big house on their acreage, but they are getting by, doing good, honest work right here in our community.
This to me is the fundamental point that speaks to the real issue behind farming in BC: they can make enough revenue on a few acres of rich ALR farmland to make a (hard) living, but they can only dream of making enough to pay for the actual land they farm, hence the short-term lease.
So the big operators are scratching by, or losing money, riding the globalized agri-business train, and the small operator is scratching by, but cannot afford to settle on a piece of land by providing better food to local people. At the same time that the majority of the food we grow, and the majority of the $2.5 Billion in annual revenue agriculture generates leaves BC, we in British Columbia spend more than $6.3 Billion on food, and watch our own farmland sit idle, or get redeveloped into tilt-up slab industrial land. Why?
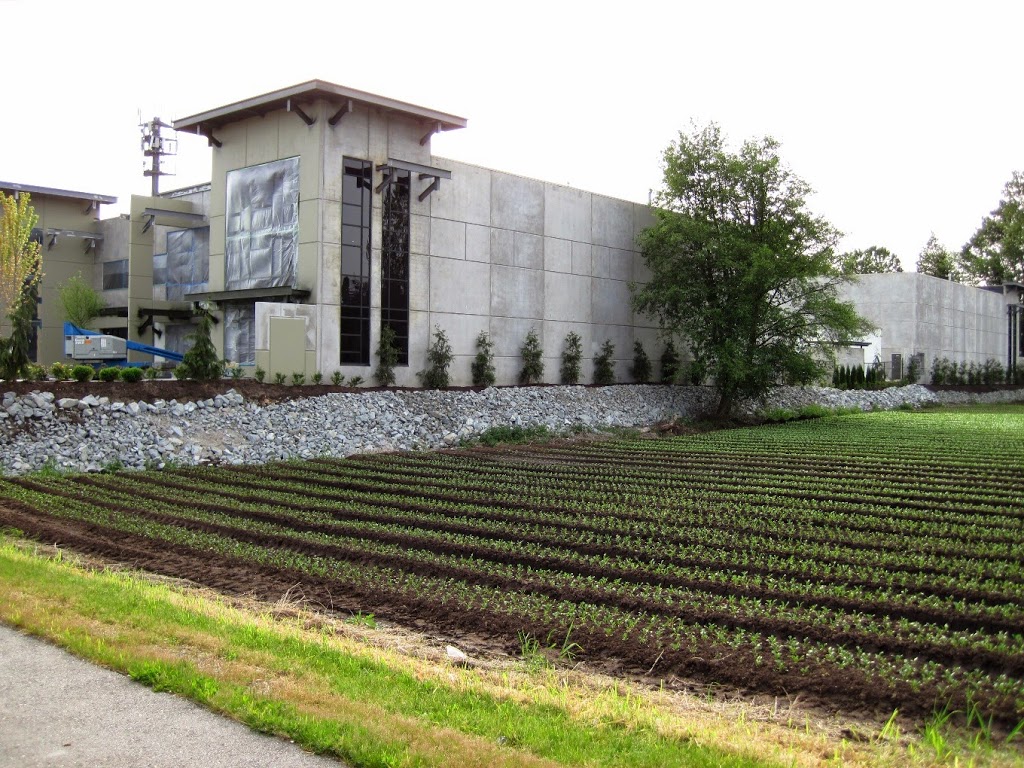 |
| A new crop of tilt-slab light industrial buildings in Burnaby. |
Because agri-business food is cheaper.
That’s it – that is the only reason anyone can give for why that slab of antibiotic-laden, nutrient-reduced, potentially-diseased, tasteless flesh wrapped in plastic at Safeway is the better way to feed ourselves. However – and this is the important point – this is a false economy.
The compromises we need to make to our food security to save that little bit of money at the check-out counter are huge, and piling up, and they don’t represent real savings, they represent offsetting costs. The reliance on increased petrochemical inputs, on overtaxed soil and contaminated water systems, on increasing livestock influenza epidemics and moving food in gigantic steel boxes across the ocean when it can be grown in our own backyard. When almost all of the money we spend on that “cheaper” food leaves the Province, and the large agri-businesses operating in BC are losing money – is this really the cheaper option? Or are we being penny wise and pound foolish.
When the California Central Valley, where most of our vegetable crops come from, is seeing its third consecutive year of critical drought; when the Ogallala Aquifer, which irrigates 1/3 of grain crops in North America, is showing signs of failure; and when the world is moving past peak phosphorous (Cripes! That’s a thing!?), there are many signs that the era of all this “cheap food” is fleeting. The system is too big, too unyielding, and relies on too many critical paths. The globalized agri-business food industry in 2012 is starting to look like a Soviet corn or cotton plan from 1960, and it is just as doomed. The economics are shifting.
If this system is breaking, what will replace it? That is what the team from the Southwest BC Bio-Regional Food System Design Project are going to try to calculate. Now this post is running very long already, so I leave it to you to go to the website and get more detail about this very interesting program (and maybe I’ll Blog more about it later). Short version: A group of researchers from Kwantlen’s Institute for Sustainable Food Systems is working with a broad group of partners including Local Governments from Hope to the Sunshine Coast and groups as diverse as the ALC, Real Estate Foundation of BC, the New Westminster Community Food Action Committee, and the Surrey Board of Trade to study the food system that nourishes our community.
Here is a quote form their website:
“The team is using a bio-regional approach to design an integrated food system that respects the boundaries and leverages the opportunities of an ecological and cultural region beyond the conventional delineations of municipal and regional boundaries. Our planning horizon is 2050. What is the potential for a revived and re-localized food system in BC; how can we respect and incorporate Indigenous harvest and hunting practices in the food system; how many jobs can we create; how much can we contribute to the regional economy; what kinds of ancillary businesses can emerge and how can this kind of food system reduce GHG emissions and address serious environmental concerns? These are some of the questions the ISFS team is trying to answer”.
This is an interesting project, in its infancy, but inside here may well be found the systems that need to be developed that will allow businesses like Urban Digs to provide food in a sustainable way to our community, and pay themselves a living wage while doing it.
Our Provincial government is also aware the ALR system is broken, but instead of fixing it, they seem intent on scattering the pieces about to prevent it’s repair. I present to you Bill 24 – Amendments to the Agricultural Land Commission Act.
The first step (and it can’t be the only one) to repair the disconnect between farm land value and its cost is to end the speculative investment in ALR land, which starts with a Government standing up and saying “This Government will not undo the ALR, and will not allow lands to be removed from the ALR”, like every other government of the last 40 years has done. Even showing the kind of commitment for the ALR that they demonstrated during the election last year would be nice. Look at their 2013 Campaign Platform, and the Agriculture section was 400 words with three strategies and 10 actions, and no mention of changes to the ALC. Actually, the platform suggests it will help with a Buy Local campaign and promote 50- and 100-mile diets, an idea that is best supported by strengthening the ALC.
This Act does quite the opposite, and opens up the door for exclusion on the whim of local politicians. The cost of farm land in the lower mainland will be going up when this bill passes, hand in hand with the pressure on local councils to open it for development.
With apologies to the most stunningly non-partisan of all Canadian scientists, this Government seems to never see a problem so bad that they can’t make worse.
Bill 24 is a potential disaster for BC food security, because it entrenches the unsustainable, failing business model that is our current globalized agri-business based food system. It not only fails to prop that business model up (as the land price equation change is going to hurt them as well!) it runs the risk of ending any hope we have of building the sustainable model that may replace it, at the very time when we are seeking to understand better what that system looks like.